Convolutional neural network (CNN)
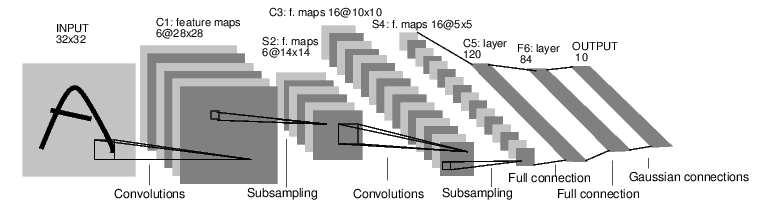
A multi-layer neural network constructed from convolutional layers.
These apply a convolution operation to the input, passing the result to the next layer.
The weights in the convolutional layers are shared, which means that the same filter bank is used in all the spatial locations.
source
Deconvolutional networks
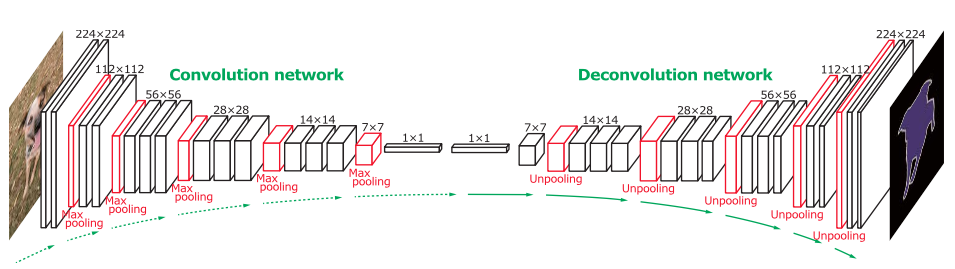
A generative network that is a special kind of convolutional network that uses transpose convolutions, also known as a deconvolutional layers.
image source
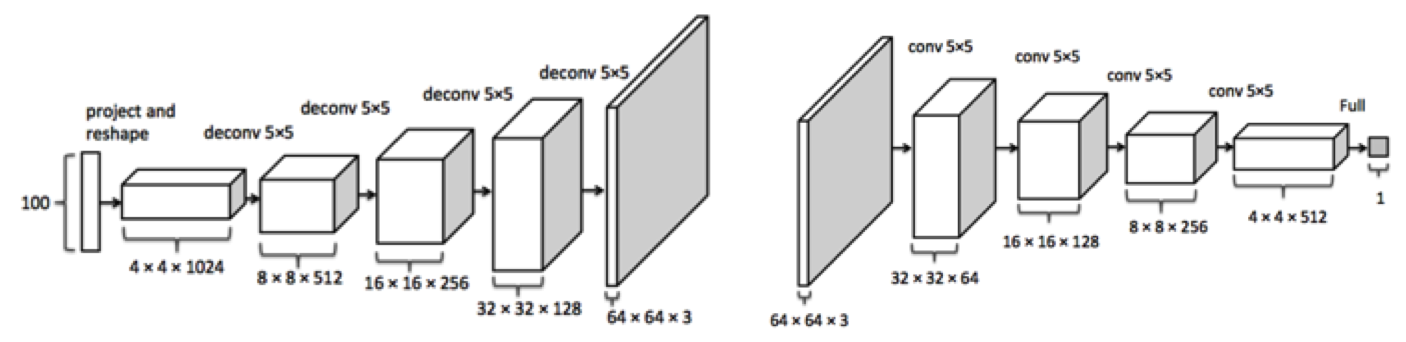
Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN)
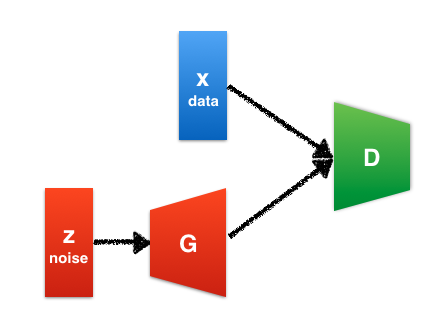 A system of two neural networks, introduced by Ian Goodfellow et al. in 2014, contesting with each other in a zero-sum game framework.
The first is a deconvolutional network, G, that generates signals.
While the second is a classifier, D, that learns to discriminates between signals from the true data distribution and fake ones produced by the generator.
The generative network's goal is to increase the error rate of the discriminative network by fooling it with synthesized examples that appear to have come from the true data distribution.
A system of two neural networks, introduced by Ian Goodfellow et al. in 2014, contesting with each other in a zero-sum game framework.
The first is a deconvolutional network, G, that generates signals.
While the second is a classifier, D, that learns to discriminates between signals from the true data distribution and fake ones produced by the generator.
The generative network's goal is to increase the error rate of the discriminative network by fooling it with synthesized examples that appear to have come from the true data distribution.
source
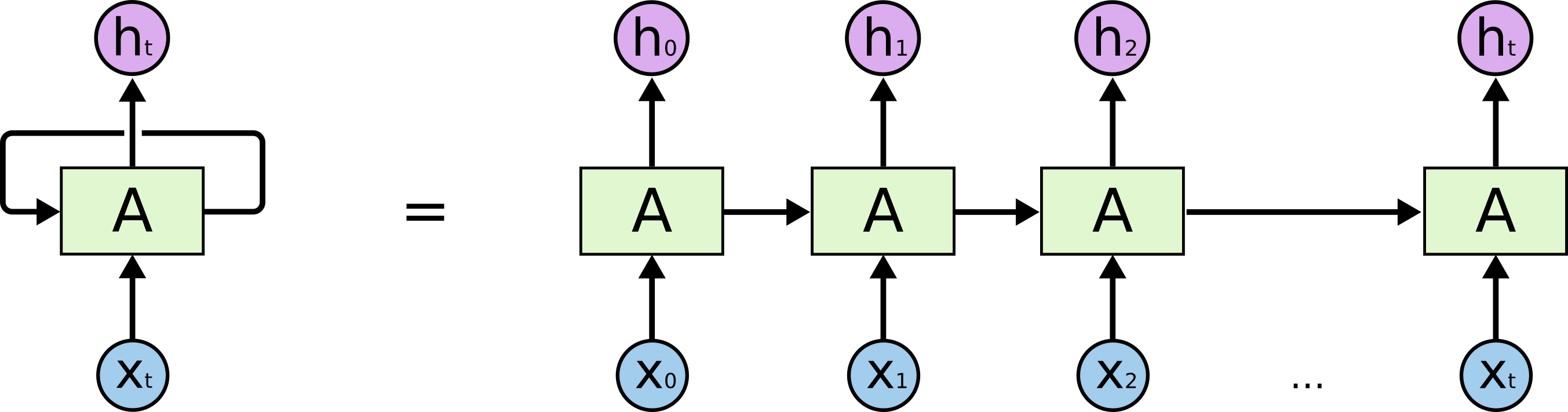
Recurrent neural networks (RNN)
RNNs are built on the same computational unit as the feed forward neural network, but differ in the way these are connected. Feed forward neural networks are organized in layers, where information flows in one direction -- from input units to output units -- and no cycles are allowed. RNNs, on the other hand, do not have to be organized in layers and directed cycles are allowed. This allows them to have internal memory and as a result to process sequential data. One can convert an RNN into a regular feed forward neural network by "unfolding" it in time, as depicted in the figures.